Dumping page for unused blocks

What does our body need?
To stay productive and healthy, we are also careful about what we consume in the form of fluids and food, but we rarely think about all the air we consume with each breath.
On average, an adult male with a sedentary occupation will breathe about 15 m3, or roughly 15 kg of air, drink 1.5 litres, or 1.5 kg, of water and eat about 0.75 kg of solid food per day. Hence, the weight of breathed air constitutes about 87% of the total biological mass turnover every 24 hours.
The evolution of human health and the indoor climate
Human beings are not adapted to the conditions or temperatures at polar latitudes, even though parts of these regions have been populated for several thousands of years.
The ideal temperature for a naked person at rest is about 29°C: a stable temperature found in the mountain and savannah landscapes of Africa, the probable origin of our ancient ancestors.
Without clothing and shelter, humans could be regarded as a tropical animal that could only survive in a narrow zone along the equator. When our ancestors migrated north, not only was proper clothing needed but a protective shield from the outdoor climate also had to be developed. From this came housing and building technology that began to evolve and adapt to very challenging winter climates.
The indoor environment is not only vital for our survival, health and well-being but has also helped the human species to thrive and spread geographically.

Carbon dioxide concentrations & effects on people
The amount of carbon dioxide in a building is usually related to how much fresh air is being brought into that building. In general, the higher the CO2 level in the building, the lower the amount of fresh air exchange. Therefore, examining levels of CO2 in indoor air can reveal if the indoor environment is good.
| CO2 levels | Probable impact |
|---|---|
| 400 ppm | Average outdoor air level. |
| 400 - 1,000 ppm | Typical level ranges found in occupied spaces with good air exchange. |
| 1,000 - 2,000 ppm | Level associated with complaints of drowsiness and poor air, often resulting in low performance. |
| 5,000 ppm | This is the permissible exposure limit for daily workplace exposures. |
| Above 30,000 ppm | Very harmful, hazard and lethal levels. |
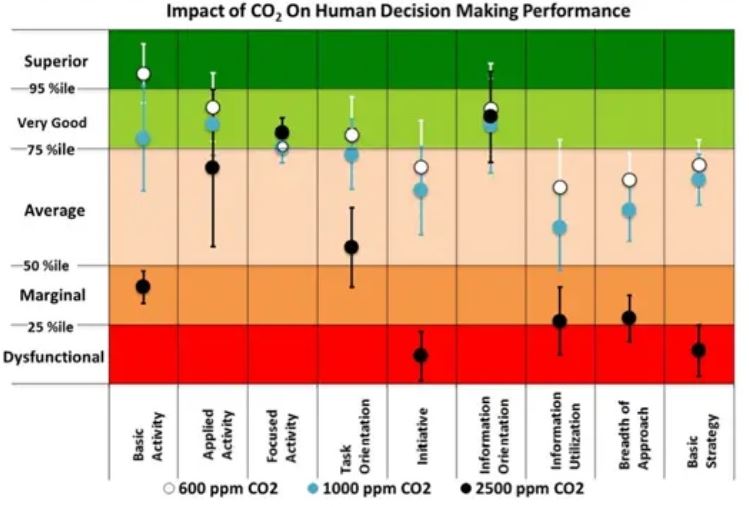
Researchers from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory found that even moderately elevated levels of indoor carbon dioxide resulted in lower scores on six of nine scales of human decision-making performance.
Everyone's reaction is different
A person's reaction to chemicals depends on several things, including individual health, heredity, previous exposure to chemicals including medicines, and personal habits such as smoking or drinking. It’s also important to consider the length of exposure to the chemical, the amount of chemical exposure, and whether the chemical was inhaled, touched, or eaten.
Temperature and productivity
Numerous different studies have been done to quantify the relationship between operating temperature and productivity. However, it is difficult to design good methods for performing this type of test. One of the more referenced studies on the relationship between air temperature and performance shows that on average, performance increases during office work with the temperature up to 21-22 ° C and then decreases by about 2% per degree temperature increase Ref. (Seppänen et al. 2006)
However, from an productivity point of view, the optimal temperature does not necessarily coincide with what is perceived as good comfort.

Buildings, like humans, need to breathe.
The reason why ventilation

There no simple solution anymore
We no longer live in times and environments where it was simple to bring fresh outdoor air to our bedrooms just by simply opening a window.
We live in times where the outdoor air is no longer what it used to be. Today, we live in places where the outdoor air quality is not good - there are high levels of various air pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), ozone (O3), sulphur dioxide (SO2), and particular matters (PM2.5 and PM10). Noise and light pollution incoming from the outdoors to our bedrooms can also disturb our sleep throughout the night.
We live in environments that are different today. We have to remember that our buildings are built in very airtight and well-insulated way - in order to be energy efficent and keep our energy bills low as there are limited natural non-renewable resources and often also due to the variety of energy crisis. Therefore the outdoor air has to be brought into our buildings in a mechanical way - as securing a good amount of airflow coming into our bedrooms is crucial to our health and well-being. And we can do that by using mechanical ventilation systems, and in this way we can also control the indoor air quality in our bedrooms to get a good night of sleep.
Types of ventilation
Natural ventilation is the process of naturally delivering and removing air from an interior space (room or building) without the mechanical assistance — only by means of natural forces, typically by wind speed, temperature and pressure differences (internally and externally).
Mechanical ventilation is the intentional fan driven flow of outdoor air into a building. Mechanical ventilation is often provided by equipment that is also used to heat and cool a space.
Hybrid (or mixed-mode) ventilation that combines natural ventilation and powered ventilation. This process allows for greater responsiveness to external conditions whiles keeping the space comfortable throughout the day and in different seasons.


We need fresh air and good ventilation
Ventilation is mainly used to control indoor air quality by diluting and displacing indoor pollutants, i.e. polluting contaminants from building and everything inside.
Ventilation is also used to control indoor temperature, humidity, and air motion to benefit and provide thermal comfort & satisfaction for buildings' living inhabitants — people, animals and plants.
We need to ventilate buildings and ventiation must satisfy several different criteria. It must be reliable, flexible, well-functioning and adaptable. And above all, it must be responsive to different needs and unusual events.
And typically, ventilation should be intentional and controlled introduction of outdoor air into an indoor space — at the right time and within the right conditions.
Under the principle of the human right to health, everyone has the right to breathe healthy indoor air.The Right to Healthy Air, World Health Organisation, 2000
Read more from other sources
Find out more from external experts Building standards in ventilation
Why We Ventilate Our Houses: An Historical Look
Nance E. Matson and Max H. Sherman
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, 2004
Extra sources to read Infitration and natural ventilation
Extra sources to read The need for mechanical ventilation
Read more from other sources Indoor climate from past to present
Read more from other sources Elements of indoor climate
