Making the indoor climate sustainable
Focusing on indoor environmental quality climate to optimise building performance and enhance people's productivity, health and well-being.
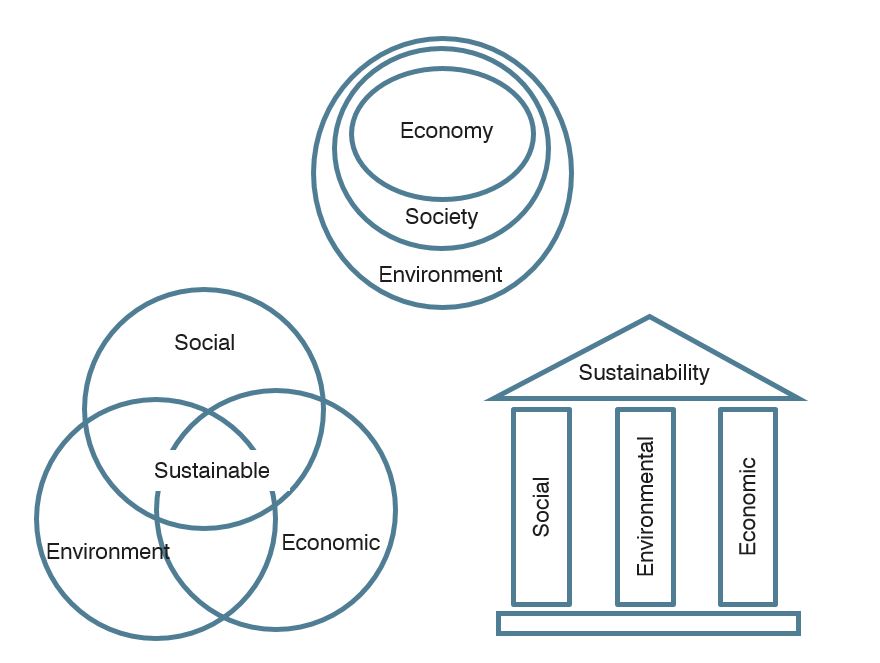
Sustainability
Sustainability is all about people co-existing on Earth over a long time.
The term sustainability is derived from the Latin word sustinere, that is "to sustain" can mean to maintain, support, uphold, or endure. So sustainability is the ability to continue over a long period of time.
Experts often describe sustainability as having three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Sustainability largly focuses on major environmental issues, including climate change, loss of biodiversity and degradation of ecosystems, depletation of natural & land sources, and air & water pollution, etc.
UNESCO distinguishes: "Sustainability is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while sustainable development refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it."
What does sustainable architecture mean?
Sustainable architecture is a general term that refers to buildings designed to limit humanity's impact on the environment.
Sustainable architecture and assessing sustainability
It all starts with a new building — with architecture and design, then comes the sustainable indoor climate.
Sustainable architecture is an eco-friendly approach to modern-day building encompassing every aspect of the planning and construction process, including: the choice of building materials; the design and implementation of heating/cooling; ventilation systems and waste systems and the integration of the built environment into the natural landscape.
Integrated design is a method for effective and sustainable building. When used throughout a building project, integrated design methods produce better buildings for both those using the building and the environment.
There is a need for practical information, data, metrics, and tools that can be incorporated into investment choices and policymaking related to sustainable, high performing building designs, technologies, standards, and codes.
Sustainability encompasses both the economics of building construction and operation as well as the environmental impacts. Evaluations are completed using a life-cycle approach and include economic performance using energy costs and environmental performance using various assesments methods.
All these and more will lead potential to the healthy environments in buildings in the future. And in forefront, there will be the implementation of technologies in the fields of energy-efficiency, indoor environment and design to achieve good indoor environment.
Dig into sustainability, architecture and design

As an architect you design for the present, with an awareness of the past, for a future which is essentially unknown.Norman Foster, Architect